




(C) 2013 Shu-Ping Sun. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 (CC-BY), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
For reference, use of the paginated PDF or printed version of this article is recommended.
A new species, Triclistus strobilius sp. n., belonging to the subfamily Metopiinae (Hymenoptera, Ichneumonidae), reared from Dioryctria pryeri Ragonot, Dioryctria rubella Hampson and Gravitarmata margarotana (Hein) in Liaoning, Hunan provinces and Beijing, is reported and described. Illustrations of the new species are provided.
Triclistus, new species, host, cone borer, Lepidoptera, Dioryctria pryeri, Dioryctria rubella, Gravitarmata margarotana, host plant
The genus Triclistus
The Palaearctic species were mainly keyed by
In the study of parasitoids that attack tree borers in three forest areas of China, a new species of Triclistus has been found. The aim of this contribution is to describe and illustrate this species and provide biological data on its habitat and hosts.
In the last five years the authors have been researching the parasitoids of borers of tree branches and cones in Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Hebei, Henan, Shanxi and Qinghai provinces, situated in the Eastern Palaearctic part of China and in Hunan and Jiangxi Provinces, situated in the northern border of the Oriental part of China.
To rear parasitoids, cones and twigs of naturally heavily infested trees of Pinus armandi Franch, Pinus massoniana Lamb., Pinus sylvestris L. var. mongolica Litv., and Pinus tabulaeformis Carr. were brought to the laboratory and maintained in large nylon cages at room-temperature. Water was sprayed over the cones and twigs twice a week and emerged insects collected daily.
The hosts were identified by Professor Hou-Hun Li, Nankai University, Tianjing, China.
Images of whole bodies were taken using a CANON Power Shot A650 IS. Other images were taken using a Cool SNAP 3CCD attached to a Zeiss Discovery V8 Stereomicroscope and captured with QCapture Pro version 5.1.
The morphological terminology is mostly that of
Type specimens and hosts are deposited in the Insect Museum, General Station of Forest Pest Management, State Forestry Administration, P. R. China.
http://species-id.net/wiki/Triclistus
Head in lateral view very thick. Face and clypeus evenly, roundly convex. Face continued dorso-medially between antennal sockets as a strong, compressed, semicircular projection, its upper end close to median ocellus, its dorso-posterior part with median concavity. Gena long, straightly convergent or very slightly incurvate backwards. Lower tooth of mandible shorter than upper tooth. Occipital carina strong and complete. Scutellum weakly convex, without lateral carina except basolateral corner. Fore wing 1cu-a distal of 1/M by 0.2–0.7 its length. Areolet usually present. Hind wing 1-cu longer than cu-a. Pterostigma broad. Epicnemial carina strong, upper end reaching anterior end of subalar prominence. Metapleuron smooth, polished. Front and mid femora rather thick. Mid tibia with two spurs. Fifth tarsomere of female with or without a ventral, subapical projection. Tarsal claw simple. Propodeal spiracle subcircular to elliptic. Metasoma short, robust. First tergite usually broad basally, its spiracle approximately at basal 0.25, its sternite reaching approximately to 0.2 length of tergum. Subgenital plate of female with or without apical-median notch. Ovipositor not projecting beyond tip of metasoma.
According to the most recent catalogue of Ichneumonoidea (
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:6EF70B06-238D-4089-827B-6D421574D72D
http://species-id.net/wiki/Triclistus_strobilius
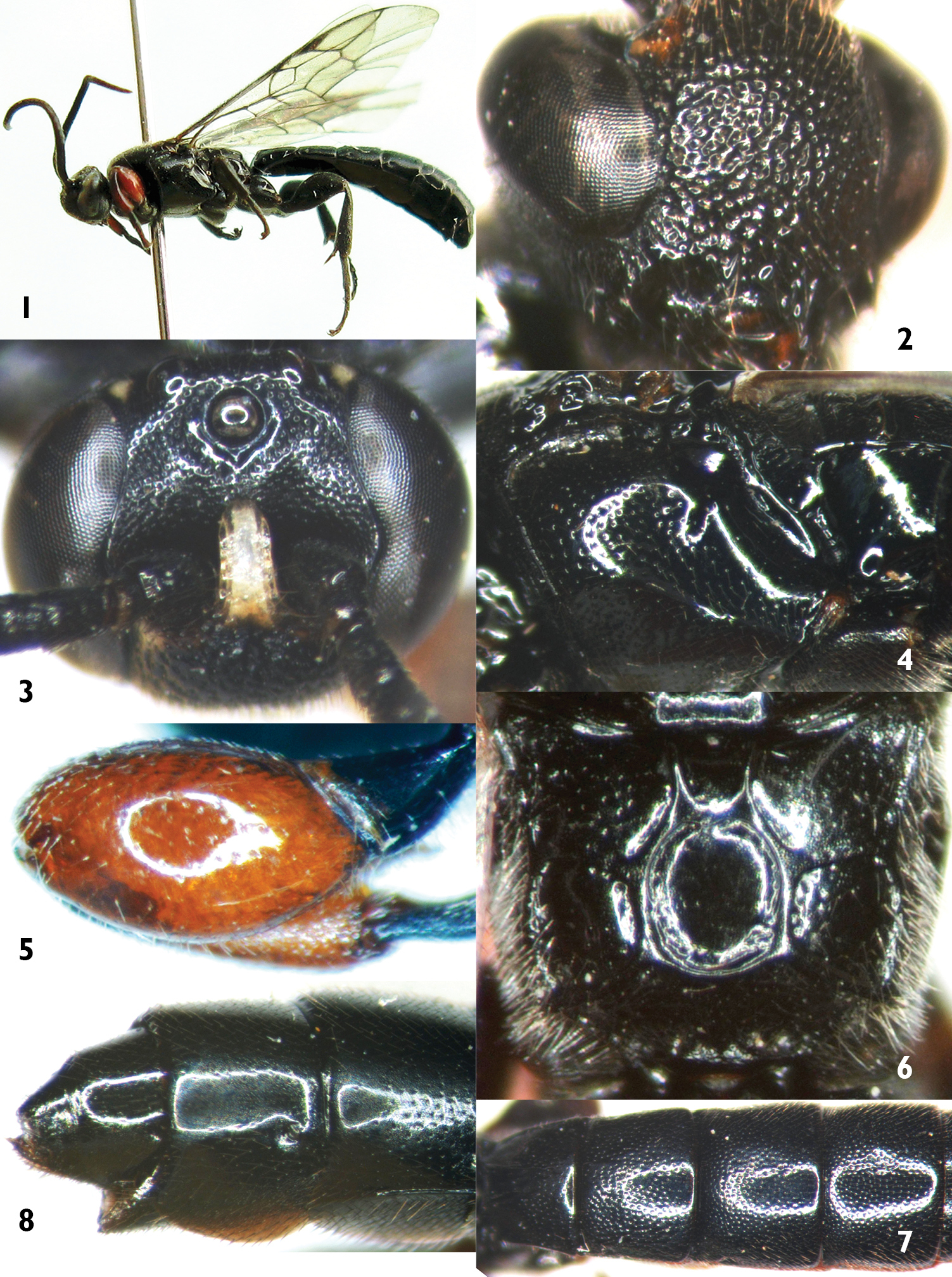
Figures 1–8Holotype, Female, CHINA: Beiling Park, Shenyang, Liaoning Province, reared from pupa of Dioryctria rubella Hampson, collected from cone of Pinus tabulaeformis Carr., 25 September 2009, Mao-Ling Sheng, Shu-Ping Sun. Paratypes: 1 female, same data as holotype; 1 female, CHINA: Beiling Park, Shenyang, Liaoning Province, reared from pupa of Dioryctria rubella Hampson, collected from cone of Pinus armandi Franch., 15 October 2010, Mao-Ling Sheng, Shu-Ping Sun; 1 male, CHINA: Fuxin, Liaoning Province, reared from pupa of Gravitarmata margarotana (Hein), collected from cone of Pinus tabulaeformis Carr., 20 October 2010, Qing-Shu Luan; 1 male, CHINA: Yanqing, Beijing, reared from pupa of Dioryctria pryeri Ragonot, collected from cone of Pinus tabulaeformis Carr., 9 July 2012, Tao Li; 1 female, CHINA: Jingzhou, Hunan Province, reared from pupa of Dioryctria rubella Hampson, collected from twig of Pinus massoniana Lamb., 1 June 2011, Mao-Ling Sheng.
Fore wing with areolet open. Tergites 2–4 (Figure 7) with approximately identical punctures. Head except whitish yellow projection between antennal sockets, mesosoma, fore and mid legs, all coxae and trochanters and metasoma, entirely black. Fore femora red.
Female. Body length 8.5–9.5 mm. Fore wing length 6.0–7.0 mm.
Head. Face (Figure 2) evenly, strongly convex, with large, dense punctures; upper median part with reddish brown hairs. Dorso-posterior part of upper-median projection with shallow median concavity. Clypeal suture absent. Median part of mandible convex, with distinct dense punctures, lower tooth very short and small; upper tooth long and sharp, approximately 3.0–3.5 times as long as lower tooth. Cheek with indistinct punctures. Malar space 0.5–0.6 times as long as basal width of mandible. Gena strongly and straightly convergent backwards, with dense punctures, distance between punctures 0.5–1.0 times diameter of puncture. Postocellar line 2.0–2.1 times as long as ocular-ocellar line. Frons (Figure 3) with dense punctures; lower part strongly concave; dorso-posterior part of projection between antennal sockets with shallow median concavity. Antenna with 31–32 flagellomeres; first flagellomere approximately 1.5 times as long as second flagellomere. Occipital carina complete and strong.
Mesosoma. Anterior margin of pronotum with fine, short longitudinal wrinkles and fine, indistinct punctures; lateral concavity wide, deep, smooth, shiny; upper-posterior margin with fine, distinct punctures. Epomia strong. Mesoscutum with fine punctures, distance between punctures 0.5–3.5 times diameter of puncture. Notaulus indistinct. Scutellum weakly convex, with texture as that of mesoscutum. Postscutellum transverse, smooth and shiny, with fine, indistinct punctures; anterior part transversely concave. Mesopleuron (Figure 4) strongly convex, with texture as that of mesoscutum; posterior part longitudinally smooth and shiny. Metapleuron almost flat, smooth and shiny, lower part with 15–20 hairs. Juxtacoxal carina absent. Submetapleural carina complete, triangularly convex anteriorly. Wings brownish hyaline. Fore wing vein 1cu-a distal of 1/M, distance between them 0.2–0.3 times length of 1cu-a. Areolet open externally. 2m-cu distal of 2rs-m, distance between them 1.25–1.3 times length of 2rs-m. Vein 2-Cu 3.0–4.0 times as long as 2cu-a. Hind wing vein 1/cu 4.0–5.0 times as long as cu-a. Front femur (Figure 5) particularly swollen, with fine, sparse punctures. Ratio of length of hind tarsomeres 1:2:3:4:5 is 10.0:4.3:3.1:1.5:2.3. Hind fifth tarsomere without subapical hook-shaped thorn. Propodeum (Figure 6) almost evenly convex, smooth and shiny, lateral sides and area petiolaris with fine, indistinct punctures, carinae complete and strong. Area superomedia separated from area basalis and from area petiolaris by strong carina, costula located slightly before its middle. Propodeal spiracle obliquely elongate, approximately 2.5–3.0 times as long as maximum width, almost touching pleural carina.
Metasoma. First tergite with even punctures between median dorsal and dorsolateral carinae, smooth and shiny between median dorsal carinae; slightly longer than apical width, weakly convergent towards sub-base, combined points of median dorsal and dorsolateral carinae projecting as lower horns, abruptly narrowed towards base of tergite. Median dorsal carinae long and strong, reaching 0.7–0.8 length of tergite. Dorsolateral and ventrolateral carinae complete. Tergites 2–4 (Figure 7) and anterior half of tergite 5 with symmetrical punctures, lateral sides almost parallel. Tergite 2 approximately 0.78–0.8 times as long as apical width. Tergite 3 approximately 0.67–0.7 times as long as apical width. Posterior half of tergite 5 and following tergites (Figure 8) with indistinct fine punctures. Posterior part of tergite 8 smooth and shiny. Apical margin of subgenital plate obtuse, without distinct apical-median concavity.
Color. Body almost entirely black (Figure 1). Upper median projection of face between antennal sockets whitish yellow. Upper margin of face faintly brown. Vertex above eye with small yellowish brown spot. Median part of mandible dark-reddish-brown. Front femora red. Apical part of front tibiae reddish brown. Front first tarsomere, apices of mid and hind tibiae, fourth and fifth tarsomeres dark red to blackish brown. Pterostigma and veins brownish black.
Male. Body length 9.0–9.5 mm. Fore wing length 6.5–7.0 mm. Upper-posterior margin of pronotum more or less yellow.
Dioryctria rubella Hampson, Dioryctria pryeri Ragonot (Lepidoptera, Pyralidae); Gravitarmata margarotana (Hein) (Lepidoptera, Tortricidae).
Pinus massoniana Lamb., Pinus armandi Franch., Pinus tabulaeformis Carr. (Pinaceae).
The name of the new species is based on the host food.
Similar to Triclistus nigrifemoralis
Triclistus strobilius, sp. n. Holotype, female. 1 Habitus, lateral view 2 Head, anterior view 3 Frons 4 Mesopleuron 5 Fore femur 6 Propodeum 7 Tergites 1–4 8 Posterior part of metasoma, lateral view.
The authors are deeply grateful to Dr. Gavin Broad (Department of Life Sciences, the Natural History Museum, London, UK) for reviewing this manuscript, and Dr. Dicky S.K. Yu (Canadian National Collection, Ottawa, Canada) for presenting valuable materials, and two anonymous referees for reviewing this manuscript. This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, No. 31070585) and Liaoning Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20102104).
